 ConfEagle
ConfEagle
ConfEagle: Automated Analysis of Security Configuration Vulnerabilities in Web Applications
Abstract
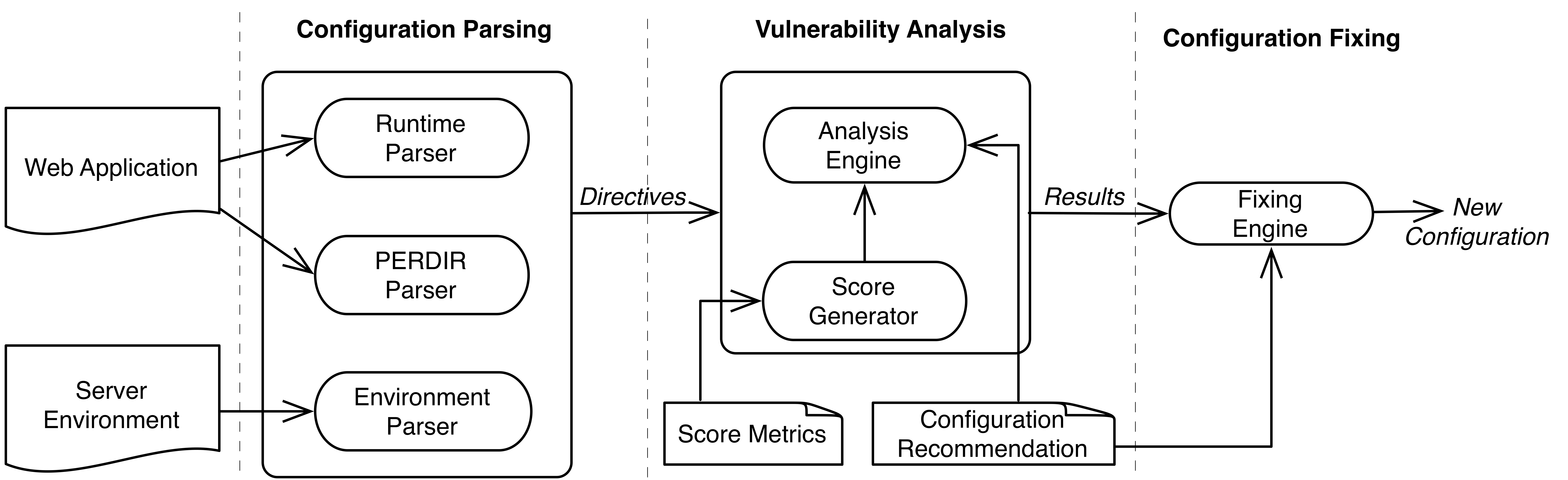
Web applications and server environments hosting them rely on configuration settings that influence their security, usability, and performance. Misconfiguration results in severe security vulnerabilities. Recent trends show that misconfiguration is among the top critical risks in web applications. While effective at uncovering numerous classes of vulnerabilities, generic web application vulnerability scanners are limited in identifying configuration vulnerabilities. In this paper, we present an approach that effectively combines hierarchical configuration scanning and preliminary source code analysis of web applications to pinpoint potential configuration vulnerabilities, quantify the degree of severity based on standard metrics, and facilitate fixing of vulnerabilities found therein. We implemented our approach in a tool called Confeagle and evaluated it on 14 widely deployed PHP web applications. Unlike generic web vulnerability scanners, on the subject applications, Confeagle detected potential configuration vulnerabilities that could result in information disclosure, denial-of-service, and session hijacking attacks on the applications.